图像超分
本文简单介绍一种底层图像任务:图像超分辨率 1。
基本概念¶
任务定义¶
图像超分辨率 (Image super-resolution, SR) 顾名思义就是将低分辨率 (low resolution, LR) 图像转化到高分辨率 (high resolution, HR) 图像的过程。可以简单地理解为全局放大。
传统超分方法在 数字图像处理 中有过介绍,根据算法的不同分为「最近邻插值、双线性插值和双三次插值」共三种。但随着深度学习技术的成熟,基于深度学习的超分性能已经显著优于传统方法。本文将全方位展开基于深度学习方法的图像超分策略。
数据集¶
首先需要明确的一点就是,超分肯定是有监督策略,即同时需要一张图像的「低分和高分」图像对,自然条件下肯定是很难获得的,但是我们可以很容易地构造出这样的图像对。具体地,这里以退化核已知的构造方法为例,将原始图像看作高分图像,然后通过双三次插值对原始图像进行下采样即可得到低分图像。
因此超分的数据集很容易获得,只要来点高分辨率图像就行了,常见用来做超分任务的数据集有:Set5、Set14、Urban100、BSD100、Manga109 等,名称最后的数字就表示该数据集的图像数量。这些数据都可以在 huggingface 上找到。
性能评估¶
在得到超分辨率图像 (SR) 后,我们需要对其进行量化评价,人工评价的方法固然可行,但是在大规模数据集上肯定不可取,这就需要一些自动评价方法。我们记超分图像为 S,高分图像为 H,宽为 w,高为 h,则针对单通道的评价指标有以下三种:
均方误差 (Mean Square Error, MSE)。如下公式:
显然 MSE 越小越好。
峰值信噪比 (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio, PSNR)。如下公式:
其中 \(\max(H)\) 表示原图的最大像素值。PSNR 单位为 dB,越大越好。
结构相似性 (Structural SIMilarity, SSIM)。
SRCNN¶
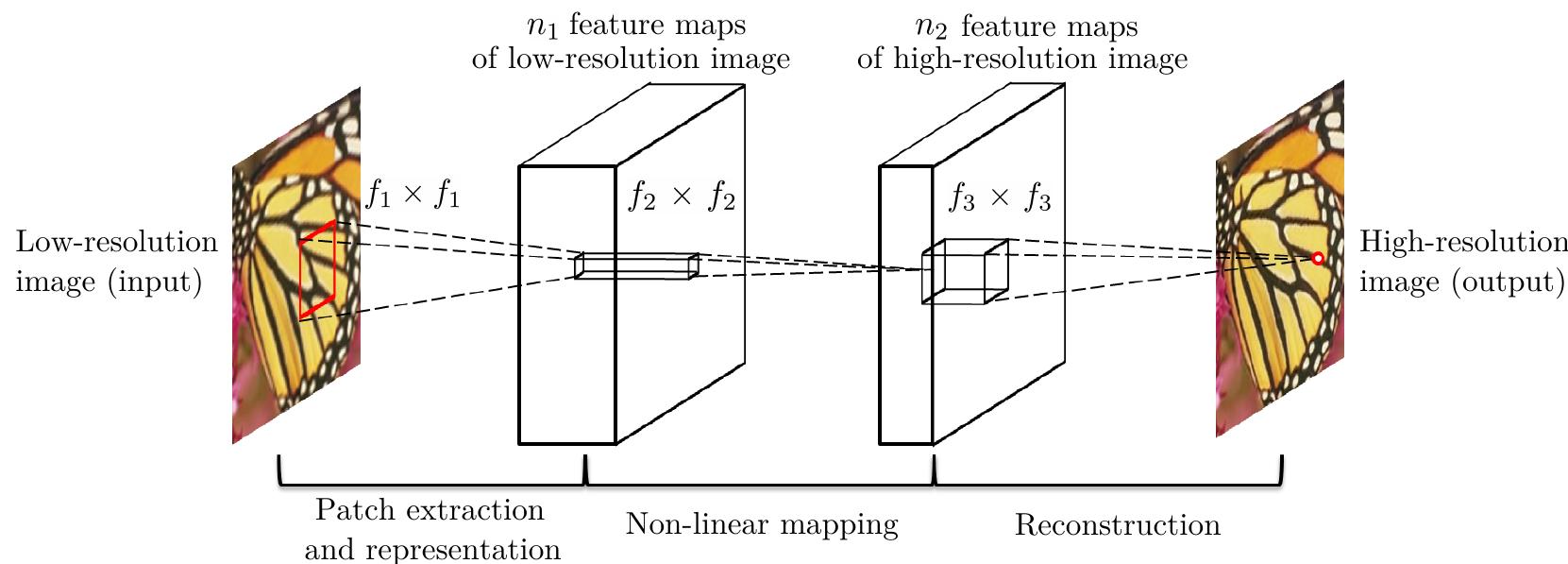
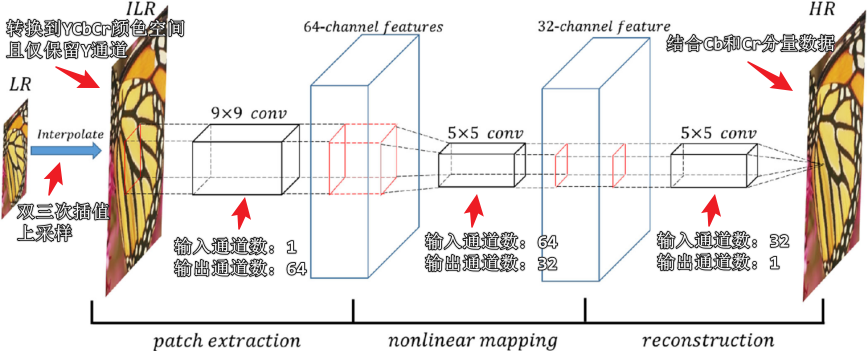
SRCNN 2 是利用深度学习方法进行图像超分的开山之作。
文中首先将 LR 利用双三次插值上采样得到了 input,接着按照上图的结构:
- 首先是一个 \(f_1\times f_1\) 卷积 + ReLU 激活操作,学习提取 LR 特征的非线性映射函数;
- 然后是一个 \(f_2\times f_2\) 卷积 + ReLU 激活操作,学习从 LR 特征到 HR 特征的非线性映射函数;
- 最后是一个 \(f_3\times f_3\) 卷积操作,学习从 HR 特征重构到 HR 的线性映射函数。
可以看出 SRCNN 仅包含卷积层且全部都是等宽卷积,不包含池化层和全连接层,SRCNN 使用 MSE 作为损失函数。整个网络的 PyTorch 代码如下:
class SRCNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super(SRCNN, self).__init__()
# 1. ILR 特征提取层
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=1,
out_channels=64,
kernel_size=(9, 9),
stride=(1, 1),
padding=(4, 4)
),
nn.ReLU(True)
)
# 2. 非线性映射层
self.map = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 32, (5, 5), (1, 1), (2, 2)),
nn.ReLU(True)
)
# 3. SR 重构层
self.reconstruction = nn.Conv2d(32, 1, (5, 5), (1, 1), (2, 2))
# 随机初始化模型权重
self._initialize_weights()
SRCNN 将 LR 图像的双三次插值结果作为 HR 图像的初始估计,这存在以下问题:
- 双三次插值的细节平滑可能会导致网络对图像细节的错误估计;
- 处理双三次插值后的图像的效率较低;
- 退化核未知的情况下,使用固定的上采样算法作为初始估计并不合理。
更窄的 SRCNN¶
SRCNN 的网络第一步通过插值将 LR 图像转化为 ILR,使得网络参数量很大,并且这有着很强的假设在里面,即默认退化核是插值的逆过程。能否直接在 LR 上学习呢?答案是可以的。
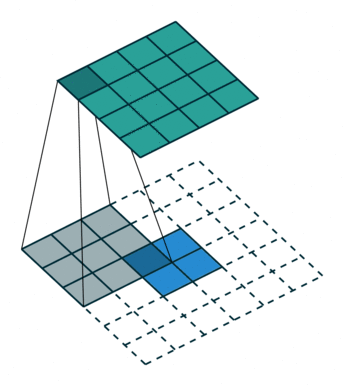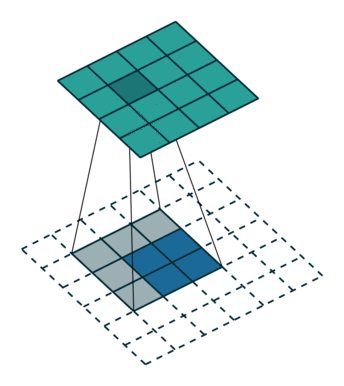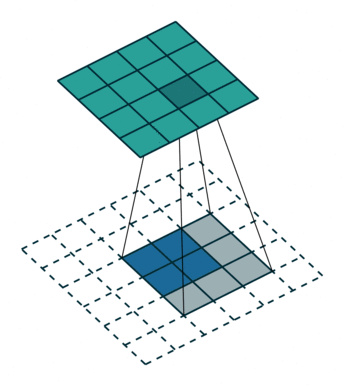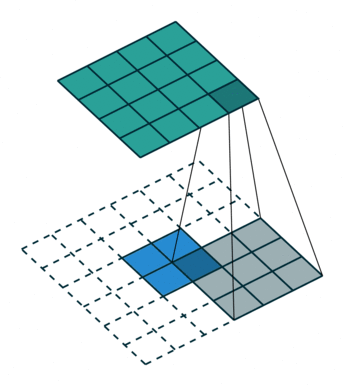
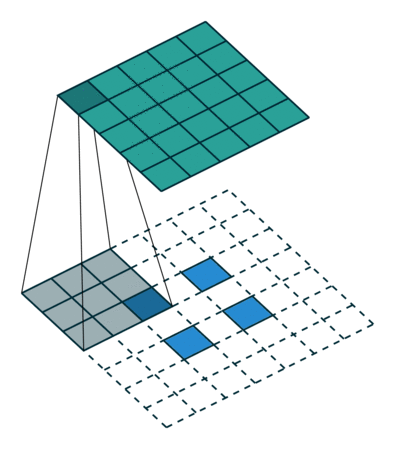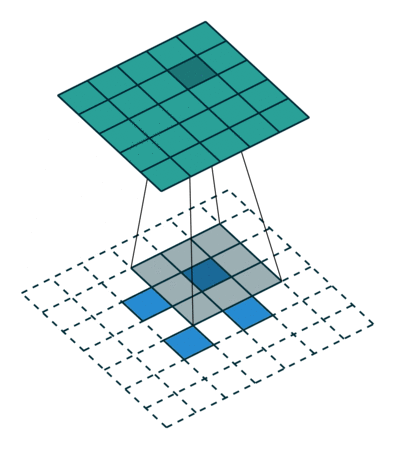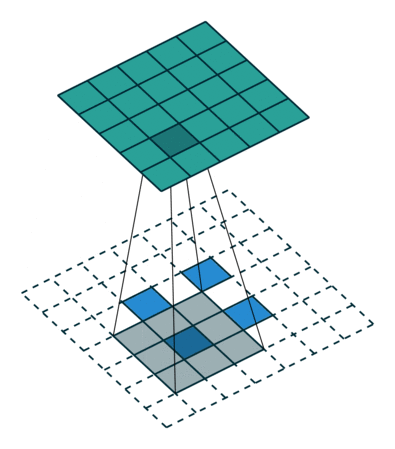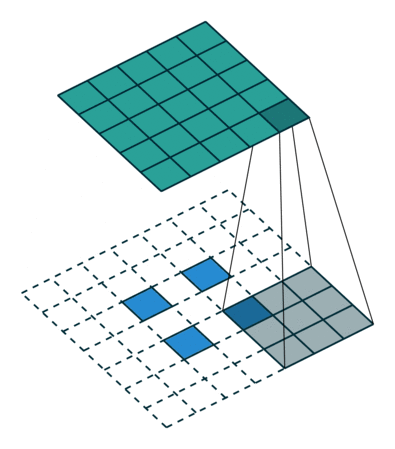
FSRCNN 3 网络采用了反卷积/转置卷积 4 策略,规避了 SRCNN 一开始的插值操作。转置卷积实例如下:
s = 1 时的转置卷积运算示例:
s > 1 时的转置卷积运算示例:
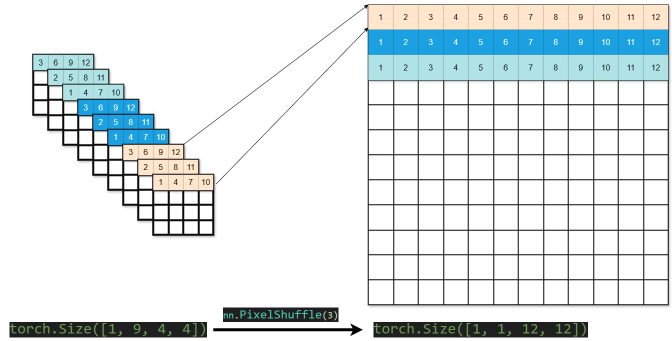
ESPCN 5 网络采用了亚像素卷积策略,同样规避了 SRCNN 一开始的插值操作。亚像素卷积实例如下:
更深的 SRCNN¶
我们知道,一般情况下,只要能解决梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题,网络越深则性能越强,为此更深的网络被提了出来。
VDSR 6 网络主要有以下几个特点:
- 结构上:采用了 VGG Net 的思想,以块为单位搭建网络,并采用「残差连接」策略防止梯度消失;
- 训练上:为了进一步提高训练速度,VDSR 采用了更大的学习率,同时使用「梯度裁剪」策略防止梯度爆炸。梯度裁剪约束了参数的梯度变化值,要么约束上下界为定值,要么进行范数放缩;
- 训练上:采用了多尺度训练策略。VDSR 没有采用反卷积或亚像素卷积,仍然采用 SRCNN 的插值策略,因此不同尺度对 VDSR 没影响,直接插值到一样的尺度就行。
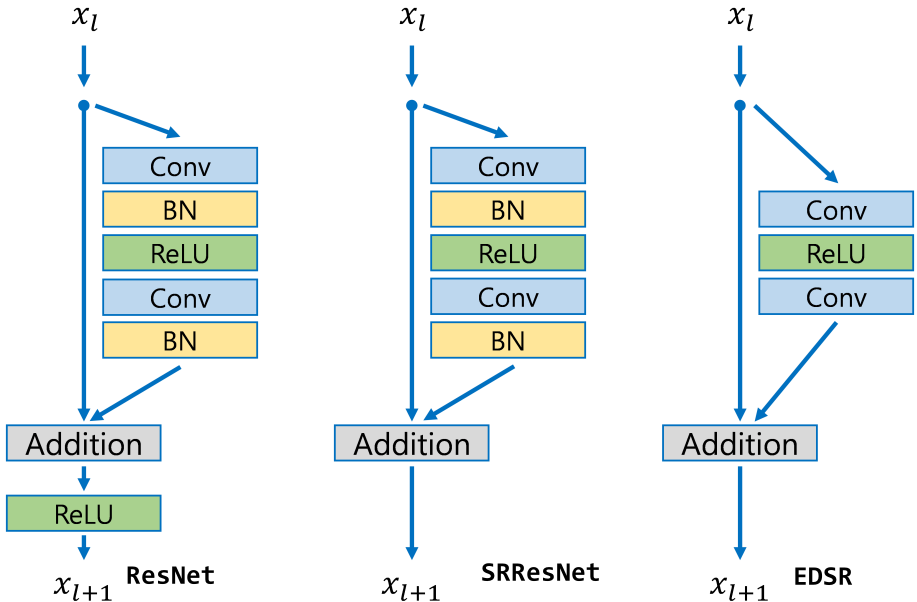
SRGAN 7 网络首次将 GAN 应用于超分任务,并基于残差结构提出了 SRResNet。
EDSR 8 网络在 SRResNet 的基础上改进了残差结构,去除了其中的 BN 层,节省了 40% 的内存,从而构建了更深的网络。同时,EDSR 认为不同尺度下的超分过程具有很强的相关性,所以提出了一种预训练策略,即在训练 \(\times 3\) 和 \(\times 4\) 的超分模型时,使用训练好的 \(\times 2\) 超分模型的参数作为初始值。
为什么超分任务不依赖 BN 操作?不妨先回看一下 GoogLeNet 引入 BN 的意义是什么:
- 对于图像分类任务而言。BN 层起到了正则化的作用,有助于提高网络的泛化能力;同时,由于特征空间和标签空间分布差异大,需要 BN 层解决 Covariance Shift 问题;
- 对于图像超分任务而言。图像超分辨率可以看作是像素的密集预测任务,图像中像素值的改变也会影响超分的结果(数据增强的方式一般只有水平翻转和旋转);同时,超分任务的输入和输出的分布差异较小,不太需要调整特征的分布。
-
Yang W, Zhang X, Tian Y, et al. Deep learning for single image super-resolution: A brief review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 21(12): 3106-3121. ↩
-
Dong C, Loy C C, He K, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]//Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, September 6-12, 2014, Proceedings, Part IV 13. Springer International Publishing, 2014: 184-199. ↩
-
Dong C, Loy C C, Tang X. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network[C]//Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 11-14, 2016, Proceedings, Part II 14. Springer International Publishing, 2016: 391-407. ↩
-
Dumoulin V, Visin F. A guide to convolution arithmetic for deep learning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.07285, 2016. ↩
-
Shi W, Caballero J, Huszár F, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016: 1874-1883. ↩
-
Kim J, Lee J K, Lee K M. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016: 1646-1654. ↩
-
Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2017: 4681-4690. ↩
-
Lim B, Son S, Kim H, et al. Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops. 2017: 136-144. ↩