语法基础
本文介绍 C++ 的语法基础。即不 include 任何库的情况下需要掌握的内容。
程序基本结构
// 导入必要的库
#include <iostream>
// 引入标准库的命名空间
using namespace std ;
// 主函数
int main () {
// 函数逻辑
cout << "Hello, C++!" << endl ;
// 必要返回值
return 0 ;
}
基本数据类型与常量
int a = 10 ; // 整型
double pi = 3.14 ; // 浮点型
char c = 'A' ; // 字符型
bool flag = true ; // 布尔型
const int MAX = 100 ; // 常量
typedef unsigned int uint1 ; // 类型别名
using uint2 = unsigned int ; // 类型别名
运算符
int a = 5 , b = 2 ;
cout << a + b << endl ; // 算术运算: 7
cout << ( a > b ) << endl ; // 关系运算: 1
cout << ( a && b ) << endl ; // 逻辑运算: 1
cout << ( a << 1 ) << endl ; // 位运算: 10
int c = ( a > b ? a : b ); // 条件运算符
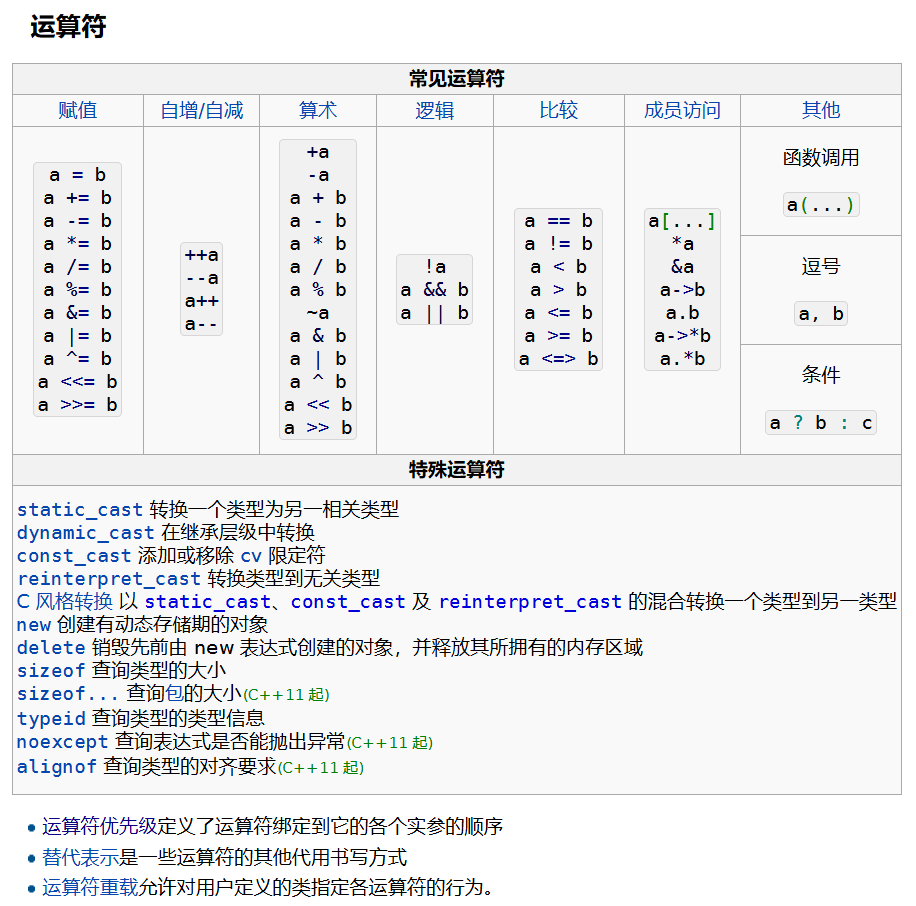
完整的 C++ 运算符 如下图所示:
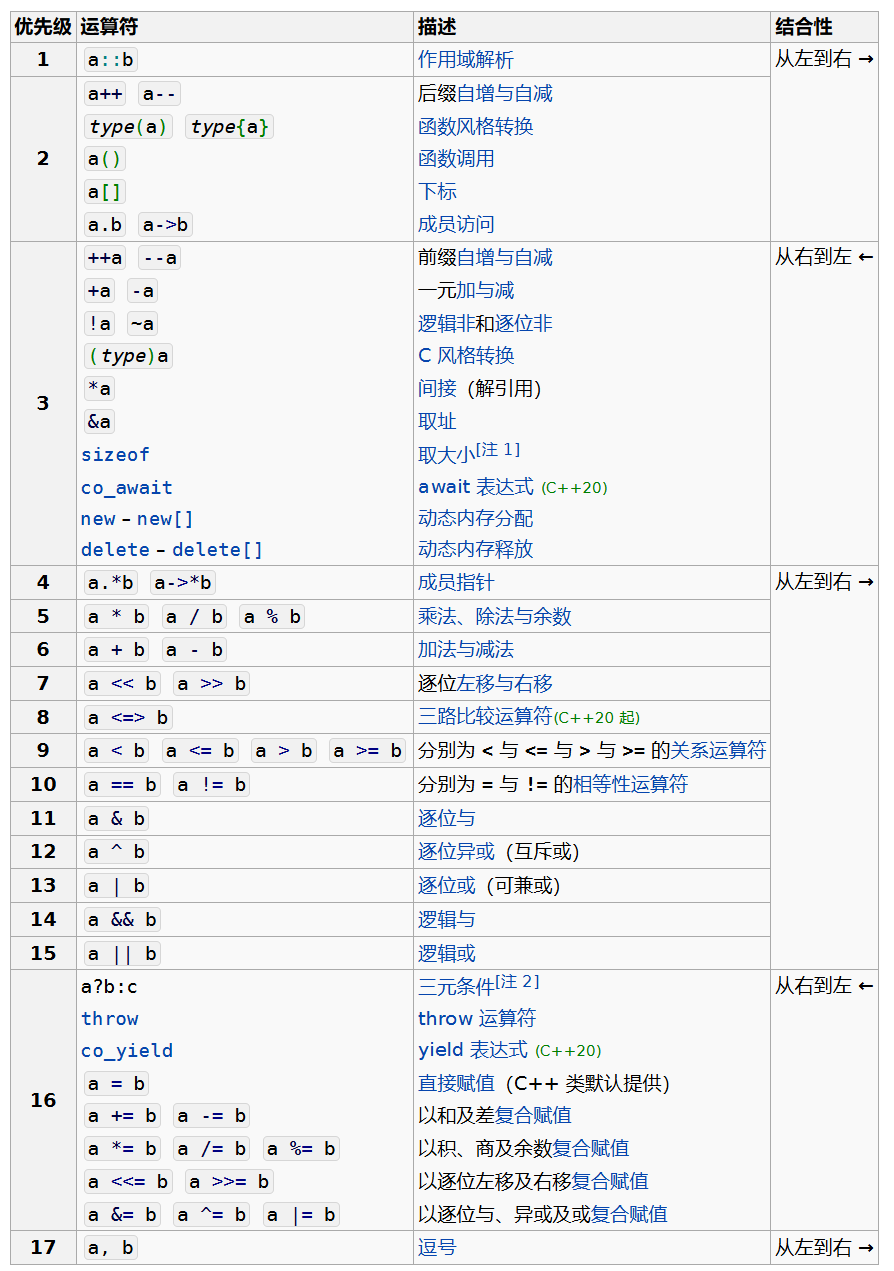
完整的运算符 优先级 如下图所示:
流程控制
分支选择逻辑:
int x = 3 ;
// if-else
if ( x > 5 ) cout << "大于5" ;
else cout << "不大于5" ;
// switch
switch ( x ) {
case 1 : cout << "one" ; break ;
case 3 : cout << "three" ; break ;
default : cout << "other" ;
}
循环逻辑:
// for
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++ ) {
cout << i << " " ;
}
// while
int j = 0 ;
while ( j < 3 ) {
cout << j ++ << " " ;
}
函数与作用域
// 默认参数
int add ( int x , int y = 10 );
int main () {
cout << add ( 5 ) << endl ; // 5+10=15
cout << add ( 3 , 7 ) << endl ; // 10
}
int add ( int x , int y ) {
return x + y ;
}
注:缺省参数只能定义在函数的声明语句中。否则会报「重定义缺省参数」的错。
原因在于,编译器在编译时只会查找「函数声明」来获取该函数的签名信息,包括参数类型和返回类型,并不关心函数体的内容。假如只在「函数定义」中定义了缺省参数,编译器在编译函数调用时就找不到对应的函数了:
数组与指针
数组。存放数的线性序列:
int arr [ 3 ] = { 1 , 2 , 3 };
cout << arr [ 1 ] << endl ; // 2
指针。指向元素的内存地址,用 32/64 位的非负整数表示:
int * p = arr ;
cout << * ( p + 2 ) << endl ; // 3
delete p ; // 手动释放
数组指针。存数组的指针:
int arr [] = { 1 , 2 , 3 };
int * parr = arr ; // parr 即指向 arr 数组首元素的指针
指针数组。存指针的数组:
写法一:
int arr [] = { 1 , 2 , 3 };
// 动态申请的指针数组
int ** pp = new int * [ 3 ]; // pp 是一个指针,指向指针数组的首地址
// 将 arr 数组中元素的地址赋给 pp 数组中的指针
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++ ) {
pp [ i ] = & arr [ i ];
}
写法二:
int arr [] = { 1 , 2 , 3 };
// 非动态申请的指针数组
int * p [ 3 ]; // p 是一个包含 3 个指针的指针数组
// 将 arr 数组中元素的地址赋给 pp 数组中的指针
for ( int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++ ) {
p [ i ] = & arr [ i ];
}
pp 和 p 是等价的。
字符串(C 风格)
char str [] = "Hello" ;
cout << str << endl ; // Hello
cout << str [ 1 ] << endl ; // e
数据捆绑
太长不看:
类型
存储方式
特点
典型应用场景
结构体 struct
每个成员独立存储
可包含不同类型的多个成员
学生信息、订单信息等实体
枚举 enum
具名常量
定义有限状态集
状态机、模式选择
联合体 union
成员共享存储
内存复用,只能存一个成员
节省内存、底层数据表示
结构体 struct:
struct Student {
int id ;
char name [ 20 ];
double score ;
};
int main () {
Student s = { 1 , "Tom" , 95.5 };
cout << s . id << " " << s . name << " " << s . score << endl ;
return 0 ;
}
特点:
可以包含不同类型的成员;
C++ 中 struct 成员默认是 public,而 class 默认是 private。
应用场景:
枚举 enum:
enum Color {
// 默认从0开始,允许指定值
RED , GREEN = 5 , BLUE
};
int main () {
Color c = BLUE ;
cout << c << endl ; // 6
return 0 ;
}
特点:
应用场景:
联合体 union:
union Data {
int i ;
float f ;
char c ;
};
int main () {
Data d ;
d . i = 10 ;
cout << d . i << endl ; // 10
d . f = 3.14 ;
cout << d . f << endl ; // 3.14
cout << d . i << endl ; // 数据被覆盖,输出未定义的内容
}
特点:
所有成员共用同一块内存空间(大小取决于最大成员);
任意时刻只能正确保存一个成员的值;
占用内存小,效率高,但需要开发者明确知道当前有效成员。
应用场景:
变体数据结构:当需要表示“同一数据的不同表现形式”时使用。例如 广义表 中,下一个指针只可能指向「下一个结点」和「子表」中的一种。
类与对象
最基本的类:
class Person {
private :
int age ;
public :
Person ( int a ) : age ( a ) {} // 构造函数
~ Person () {} // 析构函数
void show () { cout << age << endl ; }
};
int main () {
Person p ( 18 );
p . show (); // 18
}
继承:
class Animal {
public :
virtual void speak () { cout << "Animal" << endl ; }
};
class Dog : public Animal {
public :
void speak () override { cout << "Dog" << endl ; }
};
int main () {
Animal * a = new Dog ();
a -> speak (); // Dog (动态绑定)
}
预处理与宏
#define PI 3.14
#define SQUARE(x) ((x)*(x))
int main () {
cout << PI << endl ; // 3.14
cout << SQUARE ( 5 ) << endl ; // 25
}
异常处理
try {
throw 1 ;
} catch ( int e ) {
cout << "捕获异常: " << e << endl ;
}
C++11/14/17 新特性
// 类型推导
int arr [] = { 1 , 2 , 3 };
for ( auto x : arr ) {
cout << x << " " ; // 1 2 3
}
// 匿名函数
auto lambda = []( int a , int b ){ return a + b ; };
cout << lambda ( 2 , 3 ) << endl ; // 5
2025年8月30日
2025年8月30日
GitHub